As Marc Andreesen proclaimed, software is eating the world.
And in 2024, Software as a Service (SaaS) is the de-facto, dominant model for businesses to deliver software to their customers. Considering you're selling "licenses" to a copy of software, you may be wondering: what exactly is SaaS sales, and how does it differentiate from traditional software sales?
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of SaaS sales, and offers insights and strategies for effectively selling software in the competitive landscape.
Common Pricing Models for SaaS Sales
Knowing different pricing models helps you compare and choose the right business plan.
1. Freemium SaaS pricing model
The freemium model involves companies offering limited-time access to all their plans as a trial period. The idea is to showcase the potential of their products and encourage users to buy. Companies often offer trials for 7, 14, or 30 days.
However, some companies like Supademo combine a freemium model with a reverse trial, where users can try premium features before they buy.
2. Tiered SaaS pricing model
In a tiered pricing model, you can access certain features depending on your plan. Higher tiers usually offer more advanced features and also come with a higher price tag.
3. Per User SaaS pricing model
Per-user pricing plans allow you to pay based on the number of users with access to the software. As the number of team members requiring access increases, so does the overall cost.
Unlike traditional software that requires a one-time purchase and installation, SaaS solutions are hosted on the provider's servers and offer ongoing service, often including regular updates and customer support.
Traditional SaaS Sales Process

When it comes to the sales process for SaaS, it can greatly depend on the pricing model explained above. But generally speaking, the majority of SaaS companies follow the model below:
- Lead Generation: This involves identifying potential customers who might benefit from the SaaS product. Techniques include content marketing, SEO, and leveraging social media platforms. Many companies also rely on personalized prospecting at scale to solicit leads.
- Qualification of Leads: Once leads are generated, they need to be qualified to ensure they are a good fit for the product. This often involves understanding their needs, budget, and decision-making process. This typically happens through a discovery call or sales-led product demo.
- Product Demos and Trials: Offering free trials or demonstrations of the software is a common practice in SaaS sales. It allows potential customers to understand the product's value before committing. Tools like interactive demos can reduce the burden to create proof of concepts and highlight key features and benefits.
- Closing the Sale: This stage involves negotiations, addressing any concerns, and finalizing the deal. It's crucial to maintain clear communication and transparency.
- Post-Sale Support and Upselling: After the sale, ongoing support, regular updates, and upselling additional features or services become key components of the SaaS sales strategy. This includes creating demos, guides, and content that enables customer success.
Challenges in SaaS Sales
While selling SaaS is much more scalable than traditional sales processes, it's not without it's challenges. Here are some novel challenges faced when it comes to SaaS sales:
- High Competition: The SaaS market is crowded, making it challenging to stand out.
- Customer Churn: Retaining customers can be difficult in a market where switching costs are relatively low. Mitigating the impact of churn is key.
- Complex Sales Cycles: Depending on the complexity and cost of the software, the sales cycle can be lengthy and involve multiple stakeholders.

To overcome some of these SaaS sales challenges, modern sales teams should focus heavily on personalization and process to drive and convert pipeline. Here are some actionable tips on how to to find success in SaaS sales:
- Focus on Solution Selling: Highlight how your product solves specific problems or improves business processes.
- Build Strong Customer Relationships: Engage with customers regularly and offer exceptional support.
- Leverage Customer Feedback: Use feedback to continually improve the product and the sales process.
- Invest in Training Your Sales Team: Ensure your team understands the nuances of SaaS sales and can effectively communicate your product's value.
- Utilize Data and Analytics: Track customer interactions and sales data to refine strategies and identify opportunities.
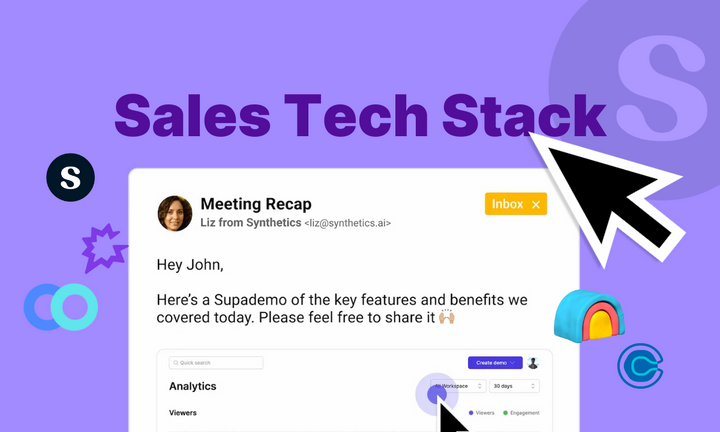
- Use a Modern Tool Stack: Platforms like Supademo are low-cost, low-effort resources to help increase and close sales pipeline. Below is an example of one in action:
Conclusion
SaaS sales require a distinct and personalized approach when compared to traditional software sales. By focusing on the customer's ongoing needs, understanding SaaS pricing models, and by personalizing sales processes at scale, companies can thrive in the competitive world of SaaS.