This guide explains what Gap Selling is, how it works, and why it helps sales teams close more deals. You’ll learn the key stages: current state, future state, and the gap between them.
It also covers practical steps, discovery questions, real examples, and how tools like Supademo make Gap Selling more effective by turning the buyer’s desired future state into an interactive experience.
You’ve likely seen it happen: a prospect sits through your demo, nods at the right points, says the product looks impressive, and then the deal goes silent.
The issue is rarely your product. More often, the buyer never felt a strong enough reason to change.
Gap Selling solves this by making that reason crystal clear.
In this guide, we’ll explain how Gap Selling works and how you can apply it to win more deals.
What is Gap Selling?
Gap Selling is a modern sales methodology created by Keenan, author of Gap Selling: Getting the Customer to Yes.
At its core, the approach is built around one simple idea: buyers make decisions when they recognize a meaningful gap between where they are today and where they want to be in the future.
Keenan sums up the difference best. In his words, selling should start with problems, not product:
"Never send your product information before you understand the buyer’s problem knowledge. When you lead with product you lose control. When you lead with problems, impact, and root cause, buyers see you as a trusted advisor who can guide them forward."
How does Gap Selling work?
Gap Selling works by guiding a prospect through three interconnected stages: their current state, their future state, and the gap between the two. The methodology is not about selling a product right away. It’s about uncovering problems, diagnosing root causes, and improving sales qualification by helping the buyer see why change is necessary.
1. Current state: what is happening today
The first step is to understand the prospect’s reality as it stands. This means asking questions about:
- Their environment (processes, tools, and team setup)
- The problems they are facing
- The impact of those problems in financial, operational, and emotional terms
- The root causes behind those challenges
- The emotions tied to the situation, such as frustration, stress, or lack of confidence
2. Future state: where they want to be
Next, the seller helps the prospect define their ideal outcome. This often includes:
- How processes should work if problems are fixed
- What business results do they expect, such as higher revenue, faster delivery, or less risk
- How the change will improve daily work for individuals and teams
- The emotional payoff, such as reduced stress, more control, or higher confidence
3. The gap: the space in between
Finally, the seller frames the gap: the measurable distance between the current and future states. This is where urgency lives. The wider and more costly the gap, the stronger the motivation to act. Sellers quantify this in terms of lost revenue, wasted time, missed opportunities, or risk exposure, and tie it to the emotions already uncovered.
By moving through these three stages, salespeople shift from product pitching to problem diagnosis. They create a clear narrative: “Here is where you are, here is where you want to be, and here is how we help you close that gap.”
What are the benefits of using Gap Selling?
Gap Selling creates value by aligning the sales process with how buyers actually make decisions. Instead of pushing features, it builds urgency and trust by showing prospects what they stand to gain — and lose — when moving from their current state to their desired future state.
Higher win rates and larger deals
When reps uncover meaningful problems and quantify their impact, they can prioritize opportunities that matter most. Small gaps rarely justify action. Large, clearly defined gaps drive urgency and make it easier to justify bigger investments.
Shorter sales cycles
Gap selling helps shorten the sales cycle. Prospects move faster when they see the cost of staying in the status quo. By defining the gap early, sellers frame the decision as time-sensitive and prevent deals from stalling in endless “maybe later” discussions.
More reliable forecasts
Gap Selling makes opportunities easier to evaluate. Since deals are tied to measurable problems and outcomes, sales teams can better predict which deals will close and when, improving pipeline visibility and forecast reliability.
Stronger relationships built on trust
This methodology positions sellers as advisors, not vendors. By showing prospects that you understand their problems and aspirations, you earn credibility. Buyers are more likely to see you as a partner who helps them succeed, which opens the door for long-term growth and accelerates sales.
How is Gap Selling different from other sales methodologies?
If you’ve used other sales frameworks before, you might wonder how the Gap Selling framework stacks up. Is it really different, or just a new label?
Let’s break down how it compares to popular approaches like Solution Selling, Challenger, Sandler, and SPIN so you can see where it fits best.
Gap Selling vs. Solution Selling
Solution Selling is about matching a product to a problem the buyer already knows. It assumes the buyer understands what’s wrong and just needs the right solution.
Gap Selling goes deeper. It uncovers hidden problems, measures their business and emotional impact, and shows the cost of staying the same. Buyers feel guided, not sold to, which builds stronger urgency.
Gap Selling vs. Challenger Selling
Challenger Selling is about teaching buyers something new and challenging their thinking. It works well when buyers underestimate their risks, but it can feel pushy.
Gap Selling is more collaborative. Reps uncover the current and future states, then define the gap together with the buyer. It works best in complex, consultative deals and is highly effective for enterprise SaaS sales, though it takes more time and stronger discovery skills.
Gap Selling vs. Sandler Selling
Sandler Selling focuses on building rapport and qualifying through pain points, budget, and authority. It often stops at surface-level issues.
Gap Selling is more structured. It digs deeper to find the root cause of problems and links them to measurable outcomes. Instead of just qualifying, it creates urgency by showing exactly what the buyer loses by not solving the problem.
Gap Selling vs. SPIN
SPIN Selling uses four types of questions: Situation, Problem, Implication, and Need-payoff. It helps uncover needs, but is narrow and mostly focused on questioning.
Gap Selling takes a broader view. It looks at the full picture: the current state, the future state, and the gap in between. This makes it easier to link solutions to real business value.
What steps can sales reps follow to apply Gap Selling in practice?
To apply the framework effectively, sales reps need to move beyond product talk and focus on uncovering what truly motivates change. Here’s a step-by-step look at how to use Gap Selling in practice.
Do research before outreach
Gap Selling doesn’t begin on the discovery call. It starts with the homework you do before you even reach out. Look into the prospect’s industry, company size, and likely challenges your product addresses. Build a problem map: what problems do you typically solve, what causes them, and how do they impact a business like this one?
By doing this upfront, you avoid wasting time on questions your prospect expects you to already know. You enter the conversation with credibility, allowing you to spend more time uncovering root causes rather than merely scratching the surface.
Uncover the prospect's current state
Once you connect with the prospect, focus on their world today. Ask about their processes, tools, and challenges. Go beyond surface issues to understand the real impact on the business and the root causes behind it.
Also, pay attention to emotions. How do these challenges make them feel—frustrated, stuck, under pressure? Capturing both business and emotional context gives you the full picture and shows you truly understand their situation.
Define the desired future state
After exploring the current state, shift the focus to what “better” looks like for your prospect. Ask them to describe the results they want, the processes they hope to improve, and what success would mean for their team.
Do not stop at vague goals like “increase efficiency.” Push for specifics: faster onboarding, fewer errors, more predictable revenue. When the buyer defines their future state in detail, it creates a shared vision you can both work toward.
Quantify the gap
A prospect may know their problems, but until those problems are translated into numbers, they lack urgency. Your role is to help them measure the cost of staying in the current state.
Ask: How many hours are wasted? What revenue is being lost? What risks are they exposed to? Then, tie those figures to outcomes that matter. For example, “delayed onboarding costs your team 40 hours per hire” or “lost renewals equal $300K a year.”
When the gap is quantified in time, money, or risk, the prospect can no longer ignore it. The abstract pain becomes a tangible business case for change.
Tailor solutions to decision-making factors
Every buyer values different things. Some focus on price, others on ease of use, speed, or risk reduction. Pay attention to what they emphasize during discovery and adapt your approach.
For example, a cost-conscious buyer needs to see ROI, while a risk-sensitive one wants compliance or security. When you position your product around the criteria that matter most, you remove friction and make the decision feel easier and safer.
Position your product as the bridge
Once you have defined and quantified the gap, your job is to guide the buyer toward the future state they want. Show them how your product takes them from today’s problems to tomorrow’s outcomes. Keep the focus on their priorities, not on listing features.
This is where interactive demos help. With demo automation tools like Supademo, you can create personalized sales demos that mirror a buyer’s workflow, highlight relevant features, and make the future state tangible. When prospects experience the solution closing their gap, the decision feels natural and low-risk.
Here's an example of an interactive demo that you can create using Supademo:
What discovery questions should sales reps ask in Gap Selling?
Gap Selling depends on discovery. The quality of the questions you ask will determine the quality of the insights you uncover. Your goal is not to rush through a script but to guide the prospect into describing their current state, their future state, and the gap in between.
Categories of Gap Selling questions
Gap Selling typically uses four types of questions:
- Probing questions to uncover details about the current situation.
- Process questions to explore how things work today.
- Provoking questions to challenge assumptions and highlight risks of inaction.
- Validating questions to confirm that you have understood the problem correctly.
Gap Selling questions examples for each stage
There is no set-in-stone list of Gap Selling questions. The best ones are always tailored to the individual prospect based on their industry, role, and specific challenges. But at a high level, here’s what questions for each stage often look like:
Current state
- What does your process look like today?
- What problems are you running into most often?
- How are these issues affecting your team’s productivity or results?
- What do you think is causing these problems?
Future state
- If you could fix one thing tomorrow, what would it be?
- What would success look like six months from now?
- How would solving this problem change the way your team works?
- What would this improvement mean for you personally?
The gap
- What is stopping you from making this change today?
- What risks do you face if nothing changes?
- How much time or money is lost because of the current approach?
- What would you gain if you reached the desired future state?
Tailoring your questions
The best discovery conversations feel natural and relevant. That means adapting your questions to both the person and their stage in the buying journey.
A VP of Sales might respond to, “How is your current process affecting your team’s ability to hit quota?” while an Operations Manager might connect more with, “How much time does your team spend fixing errors each week?”
You also need to consider the buyer’s state.
As Jen Allen-Knuth, founder of DemandJen, notes, some objections come from the current state, when the buyer doesn’t feel enough pain to act. Others come from the future state, when they see the need to change but doubt your solution or timing.
3 Real-world examples of companies using Gap Selling methodology
The real proof of Gap Selling is not in frameworks but in results. To see how this approach plays out, let’s explore how companies across industries have used interactive demos to bridge the gap and win customers.
RB2B
RB2B helps B2B companies de-anonymize website visitors in real time. As a small team, they struggled to keep up with demo requests and found that static materials did not show value clearly.
They introduced interactive demos to give prospects an instant, self-serve view of how RB2B turns anonymous traffic into qualified leads. This made the gap clear: long, manual calls versus an immediate understanding of ROI.
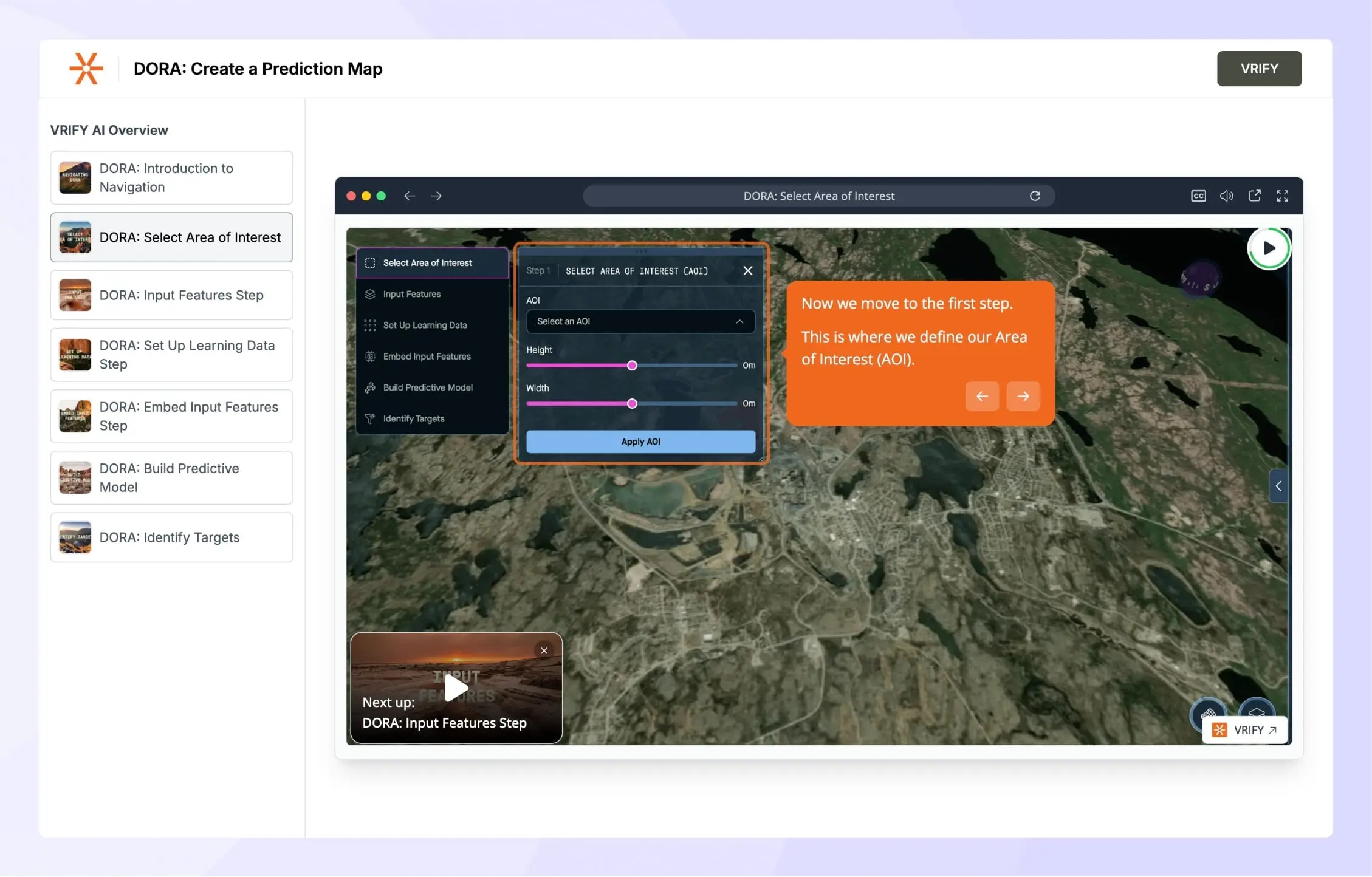
VRIFY
VRIFY, a Series B company transforming mineral exploration with AI, faced a challenge: onboarding and training were time-consuming, fragmented, and hard to scale. Manual walkthroughs slowed knowledge creation, and the team risked falling behind demand.
They introduced interactive demos to give clients and employees self-paced, visual training. This highlighted the gap between clunky static resources and an engaging, scalable onboarding experience.
beehiiv
beehiiv, a fast-scaling newsletter platform, faced a classic gap: plenty of signups, but too many were unqualified and slow to convert. The current state was friction, where prospects had to sign up before understanding the product, and videos felt passive.
The future state was a faster, clearer path to value, where customers could see for themselves how beehiiv would grow their audience.
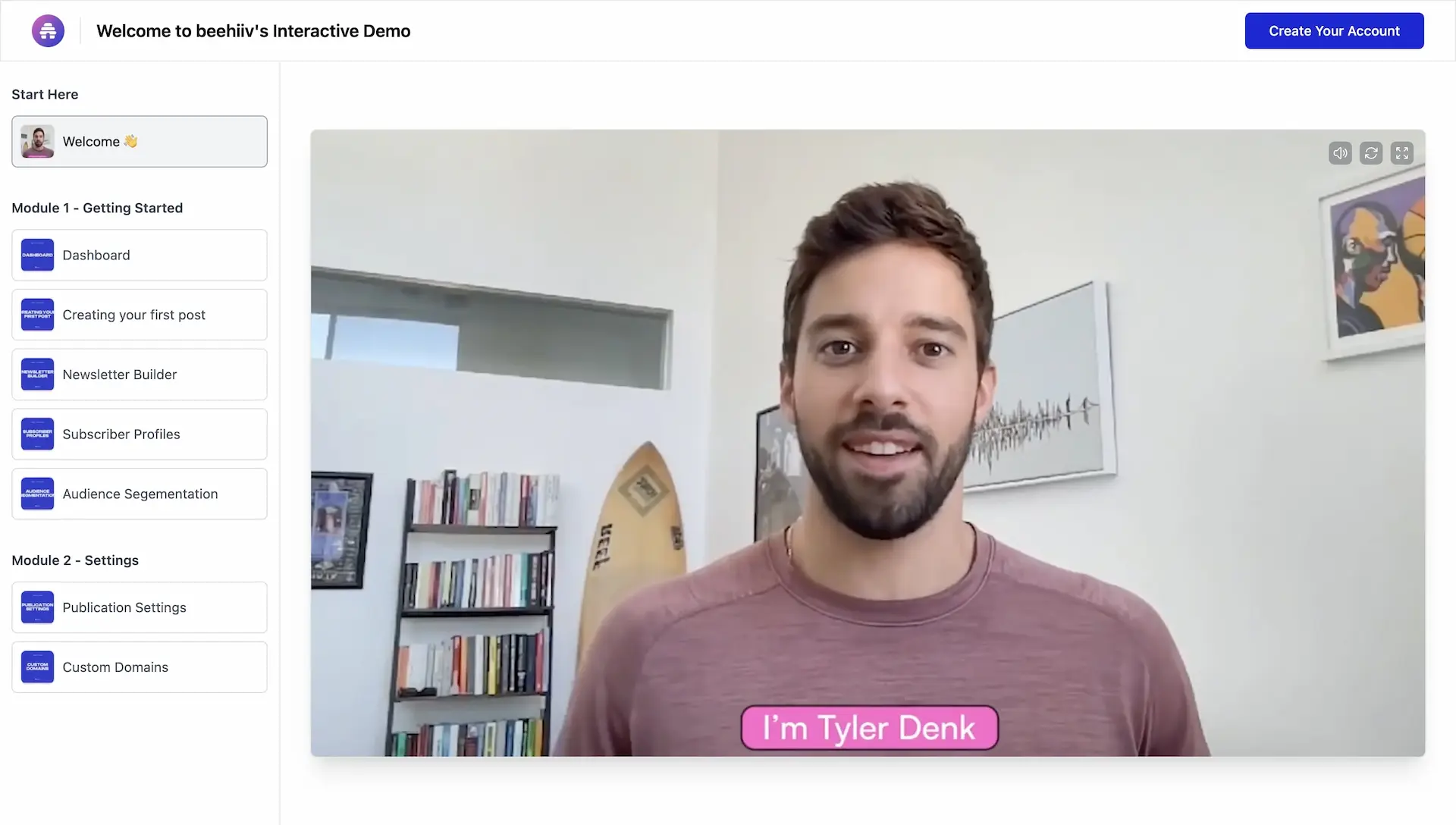
Interactive demos became the bridge. By letting prospects click through real workflows without creating an account, beehiiv made the gap visible and the future state tangible.
Bridge the gap with Supademo
At the heart of Gap Selling is showing buyers the difference between their current state and their desired future state. When that gap is visible and personal, it builds urgency, trust, and influence.
Supademo helps you make that gap tangible. Instead of explaining change with words alone, you can create interactive demos that show exactly how your product solves today’s problems and delivers tomorrow’s outcomes.
With Supademo’s no-code platform, you can quickly build click-through demos that bring discovery conversations to life, embed them in sales outreach, or share them across teams. Buyers see the future state in action, not just in theory.
And when prospects experience the value for themselves, they are more engaged, more confident, and more likely to buy.
Ready to close the gap in your sales process? Try Supademo now
FAQs
What is the main goal of Gap Selling?
The goal of Gap Selling is to help buyers recognize the gap between their current state and their desired future state. Once this gap is clear, sales teams can create urgency and position their solution as the bridge that closes it.
How is Gap Selling different from traditional selling?
Traditional selling focuses on pitching features or benefits. Gap Selling focuses on diagnosing problems, uncovering root causes, and guiding buyers toward change by quantifying what they lose by staying the same.
What are examples of current state and future state in Gap Selling?
A current state example might be “Our team spends too much time on manual reporting.” A future state example could be “We want automated dashboards that save 10 hours per week.” The space between them is the gap that motivates action.
When should sales reps use Gap Selling?
Gap Selling works best for consultative or complex sales, where understanding the buyer’s challenges and quantifying impact matters more than quick feature pitches. It’s especially effective in B2B or high-value sales cycles.