Your new sales hire just started Monday. By Wednesday, they're asking where to find the customer database. By Friday, they're wondering what problem your product actually solves. Sound familiar?
According to a study from Gartner, sales professionals forget 70% of training content within just one week. This shows that traditional one-time training sessions are no longer enough. You need a structured sales onboarding process with ongoing support to ensure new hires actually retain what they learn.
In this guide, we share the exact framework, templates, and checklists to fix this problem. You'll get new reps selling effectively much faster, instead of waiting for months.
- Structured onboarding dramatically reduces ramp-up time and improves retention compared to informal training approaches.
- Create role-specific programs for SDRs, AEs, and sales managers with different focus areas and timelines tailored to each position.
- Use self-serve training materials, interactive demo platforms like Supademo, and varied learning methods to keep new hires engaged and learning independently.
- Track key metrics like time-to-first-deal, retention rates, and activity levels to measure program success and identify improvement areas.
- Provide frequent check-ins during the first week, then reduce frequency as competency increases while maintaining consistent support.
What is sales onboarding?
Sales onboarding is your systematic process for turning new hires into productive team members. It starts before their first day and continues for 60-90 days.
A proper sales onboarding process covers the top five areas:
- Company knowledge and culture fit
- Product expertise and competitive positioning
- Sales methodology and your specific process
- Technology mastery
- Customer understanding and market knowledge.
The difference between onboarding and general orientation is the focus. Orientation covers HR basics. Sales onboarding specifically prepares reps to generate revenue.
For example, general orientation might explain your company values. Sales onboarding teaches how those values help you win deals against competitors.
Why is an effective sales onboarding process important?
Research shows that just 12% of workers believe their companies handle new hire training well. Companies with structured onboarding see dramatic improvements across every metric that matters to sales leaders.
Faster ramp-up time
Without structured onboarding, new reps take far too long to hit quota consistently. But with a proper onboarding process, you can solve this issue.
Studies show that new hires become effective at their work 3.4 months faster when they go through proper sales onboarding and training processes.
Increased sales rep retention
Strong onboarding programs deliver impressive retention improvements. Organizations with structured programs keep 58% more employees after three years.
In fact, quality onboarding can improve retention by up to 82%. Reps who feel prepared and supported stick around longer.
Improved performance and productivity
Well-onboarded reps consistently outperform those who learn on the job. The performance gap comes from confidence. Well-prepared reps handle objections smoothly, presenting features that matter and asking better discovery questions.
Research shows that reps with quality onboarding perform 38% better at their jobs compared to those without proper preparation.
Consistency and scalability
Documented onboarding ensures every new hire gets the same quality training. Your star performer's replacement receives identical preparation to your top rep.
This consistency becomes critical as you scale. You can hire multiple reps simultaneously without worrying about training quality variations when you have structured systems in place.
Steps to build a successful sales onboarding program
Building effective sales onboarding requires the implementation of specific processes in distinct phases. Each phase has particular objectives, activities, and success criteria.
Phase 1: Pre-boarding & preparation
Start onboarding one week before the new hire's first day. This preparation sets expectations and demonstrates your professionalism. New hires who receive welcome materials and clear expectations arrive more confident and engaged.
Manager pre-boarding checklist:
- Technology setup complete: Set up email, CRM access, phone system, and laptop.
- Workspace ready: Assign desk, provide supplies, and test all equipment.
- Welcome package sent: Include company swag, team directory, and first-week schedule.
- Mentor assigned: Choose an experienced rep who volunteers for a mentoring role.
- First-day agenda created: Plan specific activities for the entire first day.
- Manager calendar blocked: Reserve time for check-ins and training sessions.
New hire pre-boarding packet checklist:
Phase 2: Initial orientation & company culture
Week one focuses on company fundamentals and relationship building. Your goal is to help new hires understand how your organization works.
Day 1 orientation goal:
- 9:00-9:30 AM: Welcome meeting with the direct manager
- 9:30-10:30 AM: HR essentials (benefits, policies, systems)
- 10:30-11:00 AM: Coffee with an assigned mentor
- 11:00-12:00 PM: Company history and culture presentation
- 1:00-2:00 PM: Department overview with sales leadership
- 2:00-3:00 PM: Meet the broader team (marketing, customer success, product)
- 3:00-4:00 PM: Workspace setup and initial system access
- 4:00-4:30 PM: Day one wrap-up and next-day preview
Week 1 relationship-building activities:
- Coffee chats: Schedule 30-minute informal meetings with 5-7 key colleagues
- Team lunch: Arrange a group meal with the immediate sales team
- Cross-department introductions: Brief meetings with marketing, support, and product teams
- Executive meet-and-greet: 15-minute conversation with VP of Sales or CEO
- Mentor relationship kickoff: Structured first meeting with the assigned mentor
To make this orientation process more engaging, you can use a platform like Supademo to create an interactive employee onboarding kit that walks new hires through company systems, culture highlights, and role-specific tools in a guided, clickable format:
Phase 3: Core sales training & skill development
Weeks 2-3 cover fundamental sales skills and your specific methodology. Focus on practical application rather than theoretical concepts.
Here’s an example of a core sales training curriculum:
Build muscle memory through consistent practice. Short, focused sessions work better than marathon training days.
- Monday: Discovery question role-play (30 minutes)
- Tuesday: Objection handling scenarios (30 minutes)
- Wednesday: Product demo practice (45 minutes)
- Thursday: Call review and feedback (30 minutes)
- Friday: Weekly skill assessment (60 minutes)
Phase 4: Product/service knowledge & market acumen
In weeks 3-4, your reps need to move beyond features and become trusted advisors. That requires two things: strong product knowledge and confidence in competitive positioning.
Here’s an example of a product knowledge development plan:
Many teams struggle here because traditional training—screenshots, decks, and static guides—fails to show how customers actually experience the product. The result is a gap between what reps learn internally and what they need to demonstrate in real sales conversations.
Interactive product demos solve this problem by letting new hires explore your product from the customer's perspective.
Tools like Supademo let you capture actual product workflows and turn them into clickable, guided experiences. New reps can practice navigating features, understand user flows, and see exactly what customers see when they evaluate your solution.
This approach significantly reduces product training time while improving understanding and retention.
But along with product knowledge, proper competitor research also helps reps position your solution effectively and handle comparison questions confidently. Here’s how you can help with that:
- Top competitors: Create detailed comparisons of features, pricing, and positioning strategies.
- Reference guides: Develop quick reference guides for competitive situations and objection responses.
- Win/loss analysis: Review recent deals won and lost against each competitor with specific lessons.
- Differentiation messaging: Learn unique value propositions and competitive advantages for each scenario.
- Competitive objection handling: Practice specific responses to competitor-related concerns and comparisons.
Phase 5: Technology & tool training (CRM, sales enablement)
Week 4 focuses on technology mastery. Efficient tool usage directly impacts sales productivity and data quality.
Technology competency determines how much time reps spend on administrative tasks versus selling activities. Reps who master your tech stack early can focus on revenue generation instead of struggling with systems.
CRM proficiency forms the foundation of sales success. Your CRM contains customer history, pipeline data, and performance metrics. Reps who can't navigate CRM effectively miss opportunities and provide poor customer experiences.
CRM proficiency requirements:
Start with basic navigation and progress to advanced features. Ensure new hires can find information quickly and enter data accurately.
- Basic navigation: Find contacts, accounts, opportunities, and reports within 30 seconds.
- Data entry standards: Learn required fields, naming conventions, and update frequency requirements.
- Pipeline management: Update deal stages, probability, and close dates accurately and consistently.
- Activity logging: Record calls, emails, meetings, and next steps with proper detail and context.
- Report generation: Create standard reports for personal performance tracking and manager reviews.
- Automation setup: Configure email sequences, task reminders, and follow-up workflows.
Example sales tool training schedule:
Before moving to practical application, new hires must demonstrate specific technology skills. For instance, you can create clear pass/fail criteria for each tool:
- CRM data entry: Achieve 95% accuracy on contact and opportunity creation.
- Report generation: Successfully created weekly activity and pipeline reports.
- Demo creation: Produce 3 different demo variations for different customer types.
- Email automation: Configure personal sequences with proper follow-up timing.
- Proposal workflow: Complete sample proposal from template to signature.
Phase 6: Mentorship, shadowing, & practical application
Week 5-6 transitions from learning to doing. New reps observe experienced colleagues and begin hands-on practice.
Effective shadowing requires structure and clear learning objectives. Random call listening provides limited value compared to organized observation with specific focus areas.
Example of shadowing activity schedule:
Tip: Provide structured worksheets for each shadowing session. This ensures new hires focus on specific learning objectives rather than passive listening.
Now, here’s how you can structure mentorship meetings:
Weekly 60-minute sessions with the assigned mentor create consistent support and relationship development.
- Week 1: Goal setting and relationship building, establish communication preferences and meeting cadence.
- Week 2: Shadowing debrief and initial practice planning, review observations and identify focus areas.
- Week 3: Role-play scenarios and skill development, practice difficult conversations and objection handling.
- Week 4: First live call preparation and practice, review customer research and call planning.
- Week 5: Call review and improvement planning, analyze performance and identify development opportunities.
- Week 6: Independent activity planning and ongoing support, establish a long-term mentoring relationship.
Tip: Gradual increase in responsibility builds confidence while maintaining quality standards. Start with internal role-play sessions where new hires can make mistakes safely. Progress to live customer interactions with increasing independence as skills develop.
Phase 7: Ongoing support & continuous learning
Months 2-3 provide structured support as reps become independent. However, ongoing support is still essential. Most programs end after initial training, leaving new hires to figure out complex situations alone.
Create personalized growth plans that address specific strengths and development areas for each new hire.
30-Day Development Goals: Set realistic activity targets that build momentum without overwhelming new reps. Focus on consistent execution rather than immediate results.
- Activity targets: 20 outbound calls per week, 5 demos per week, 2 discovery calls.
- Skill focus: Improve discovery questioning, master competitive positioning, and handle basic objections.
- Knowledge gaps: Learn advanced product features, understand enterprise use cases, and industry knowledge.
- Support needs: Weekly manager check-ins, peer mentoring, and additional competitive training.
60-Day Development Goals: Increase expectations as competency grows. Begin measuring business outcomes alongside activity metrics.
- Performance targets: Generate 2 qualified opportunities, advance 1 deal to the proposal stage.
- Skill advancement: Handle objections independently, customize demos effectively, and manage complex deals.
- Relationship building: Establish rapport with 10 key prospects, expand internal network.
- Process mastery: Complete full sales cycle with minimal guidance, contribute to forecasting.
With Supademo integrated into your LMS, reps get quick, interactive guidance for handling objections, refreshing product knowledge, or customizing a demo exactly when they need it.
Phase 8: Evaluation & feedback
Regular assessment ensures onboarding effectiveness and identifies improvement opportunities.
Structure formal reviews to cover all aspects of performance and development. Use consistent frameworks to enable comparison across different new hires:
- 30-Day Checkpoint: Focus on knowledge acquisition and skill development. Assess whether new hires have solid foundations for continued growth.
- 60-Day Review: Shift focus to performance metrics and customer impact. Evaluate whether new hires are progressing toward quota achievement.
- 90-Day Evaluation: Assess overall onboarding success and long-term potential. Determine whether new hires are on track for sustained success.
Gather input from multiple sources to create a detailed understanding of onboarding effectiveness and individual progress.
- Regular feedback from new hires: This helps identify program gaps and improvement opportunities.
- Manager assessment: It provides a professional perspective on skill development and performance trajectory. Weekly check-ins during early onboarding create data points for trend analysis.
- Mentor feedback: It offers peer-level insights into confidence, cultural fit, and practical skill application. Mentors often identify challenges that managers miss.
- Customer feedback: This validates external competency and professionalism. Brief surveys after early interactions provide an objective assessment of new hire readiness.
Sales onboarding best practices
Successful onboarding programs share common characteristics. These proven practices help you build programs that consistently produce high-performing sales reps:
Create a structured onboarding plan (ideally self-serve)
Documentation and self-service capabilities reduce manager workload while ensuring consistency across all new hires.
Self-serve components allow new hires to learn at their own pace and revisit important concepts when needed. For example, create a digital portal where reps can access training videos, complete assessments, and track their progress through each onboarding phase.
Essential self-serve elements include:
- Video library: Record key training sessions for on-demand viewing with search functionality
- Interactive checklists: Digital workflows that track completion and guide next steps
- Knowledge base: Searchable repository of policies, procedures, and frequently asked questions
- Practice environments: Safe spaces to experiment with CRM and other tools using sample data
- Progress dashboards: Visual tracking of milestones completed and upcoming requirements
Utilize varied training methods
Different people learn through different approaches. Combine multiple methods to maximize retention and prevent boredom during lengthy programs.
Hands-on practice delivers the highest retention because it engages multiple senses and creates muscle memory. Role-playing scenarios prepare reps for real situations while interactive content keeps attention better than passive videos.
For instance, instead of just explaining objection handling, have new hires practice with recorded customer scenarios, then role-play with experienced reps, and finally shadow live calls. This progression builds confidence through varied exposure.
Integrate technology early and effectively
Technology competency directly impacts sales productivity and customer experience. Get new hires comfortable with your entire tech stack during their first week.
Start with essential systems like email and CRM on day one, then add sales-specific tools like demo platforms and email sequencing software. Create specific competency tests for each platform rather than just providing overviews.
For example, require new hires to create a complete customer record in your CRM, build a 5-email sequence in your outreach tool, and produce an interactive demo for a specific customer scenario. These practical exercises ensure real proficiency.
Set clear expectations and KPIs
Specific, measurable goals help new hires understand success criteria and track progress objectively.
Create 30-60-90 day plans with exact numbers and timelines. For instance, month one might require 15 calls per week and passing product knowledge assessments. Month two could target 2 qualified opportunities and 25 weekly calls.
Document these expectations in writing and review them weekly. New hires should never wonder if they're meeting standards or falling behind targets.
Provide continuous feedback and coaching
Regular feedback prevents small issues from becoming major problems. Create structured feedback loops that decrease in frequency as competency increases.
Start with daily 15-minute check-ins during week one, transition to weekly 45-minute sessions for month one, then move to bi-weekly meetings. Focus on specific behaviors rather than general observations.
For example, instead of saying "improve your demos," provide specific guidance like "slow down during feature explanations, pause for questions after each benefit, and confirm understanding before moving to the next section."
Foster a supportive environment
New hire success depends on feeling welcomed and supported by the entire team. Create multiple touchpoints for relationship building and assistance.
Assign both a formal mentor for skill development and an informal buddy for cultural integration. The mentor handles performance coaching while the buddy answers basic questions and provides social connection.
Encourage questions through regular availability and team interactions. New hires should feel comfortable seeking help without appearing incompetent or unprepared.
Make it engaging and interactive
Traditional learning leads to poor retention and low engagement. Build interactivity into every training component to maintain attention and improve comprehension.
Replace static presentations with interactive demo experiences. Instead of showing product screenshots, let new hires click through actual workflows, creating engaging, self-paced exploration opportunities.
Add gamification elements like progress badges, completion certificates, and friendly competitions between new hire groups. These elements maintain motivation during challenging learning periods while building team relationships.
How long should sales onboarding take?
Onboarding duration depends on your product complexity, sales cycle length, and market sophistication. Most successful programs follow predictable timelines based on these factors.
Timeline considerations by complexity:
- Simple SaaS Products (30-45 days): Basic software with short sales cycles and straightforward value propositions requires focused but shorter onboarding periods.
- Mid-Market Software (60-75 days): Moderate complexity solutions with multiple features and stakeholder involvement need additional time for comprehensive preparation.
- Enterprise Solutions (90-120 days): Complex platforms with extensive customization and long sales cycles require comprehensive onboarding with ongoing support.
Tailoring your sales onboarding process
Different roles, experience levels, and working arrangements require customized onboarding approaches. Role-specific customization ensures training relevance and efficiency.
Onboarding SDRs vs. AEs vs. sales managers
Each role has distinct responsibilities and success criteria. Customize your onboarding process based on these role-specific requirements:
- Sales Development Representatives: Need heavy emphasis on prospecting, qualification, and lead generation with a focus on activity metrics, call techniques, and email outreach strategies.
- Account Executives: Require deeper product knowledge, competitive positioning, and deal management skills with an emphasis on consultative selling, proposal development, and negotiation techniques.
- Sales Managers: Need leadership training, coaching skills, and performance management capabilities in addition to sales fundamentals with training on team development and sales process optimization.
- Experienced hires: Can move through product and process training faster but may need more time to understand your specific market and customer base.
Onboarding remote or hybrid sales teams
Remote onboarding demands intentional structure and relationship building. Here are some important things to consider while structuring the onboarding process for remote or hybrid sales teams:
- Communication frequency: Schedule more frequent check-ins and provide multiple communication channels for different types of questions and support needs.
- Face-to-face interaction: Use video conferencing whenever possible with virtual coffee chats and team meetings to build relationships that might naturally form in office settings.
- Self-serve resources: Interactive demos and self-serve training materials become even more important for remote teams who need easy access to training resources they can use independently.
- Virtual shadowing: Create observation opportunities through call recordings and screen-sharing sessions so remote reps can still learn from experienced colleagues through technology.
Measuring the success of your sales onboarding program
Effective measurement helps you identify what's working, what needs improvement, and where to invest additional resources.
Key metrics to track
Monitor these essential performance indicators to gauge program success:
- Time-to-first-deal: Measures how quickly new hires close their first sale and indicates how well your onboarding prepares reps for real selling situations.
- Ramp time to quota: Tracks how long it takes new hires to reach full productivity with effective onboarding significantly reducing this timeline.
- First-year retention rates: Shows whether new hires feel prepared and supported enough to stay through initial challenges with high turnover often indicating onboarding problems.
- Performance metrics: Activity levels, conversion rates, and deal sizes help identify specific skill gaps that onboarding should address.
- New hire satisfaction scores: Provide direct feedback on the onboarding experience and highlight areas for improvement.
Calculating ROI
Onboarding ROI calculation justifies program investment and identifies improvement opportunities. Start by calculating total program costs including training materials, manager time, and external platforms.
For example, if your program costs $15,000 per rep but reduces ramp time by three months, calculate the revenue impact. A rep earning a $20,000 monthly quota who becomes productive three months faster generates $60,000 in additional revenue.
Factor in retention savings from reduced turnover. Add manager time savings when structured programs reduce hands-on training requirements.
You can also track the long-term career progression of well-onboarded reps. Reps with strong initial training often achieve higher performance ratings and receive promotions faster, creating additional value for your organization.
Common challenges in sales onboarding
Even well-designed onboarding programs face predictable challenges. Recognizing these issues early helps you address them before they impact results:
- Information overload: New hires receive too much information too quickly and struggle to retain or apply it effectively with solutions including breaking content into digestible chunks and reinforcing key concepts repeatedly.
- Lack of practical application: New hires learn concepts but struggle to apply them in real situations requiring plenty of role-playing, simulations, and low-stakes practice opportunities.
- Inconsistent delivery: Some new hires receive excellent onboarding while others get minimal attention with standardized programs and materials helping ensure consistency across managers.
- Outdated materials: Frustrate new hires and provide incorrect information requiring regular reviews and updates to keep onboarding content current and accurate.
- Insufficient follow-up: New hires struggle without ongoing support after initial onboarding with structured check-ins and continuing education programs addressing this gap.
Sales onboarding tools and resources
The right technology improves onboarding efficiency and effectiveness. Choose tools that streamline training delivery and provide measurable results:
CRM systems
Your CRM forms the foundation of sales productivity. New hires must become proficient in data entry, pipeline management, and reporting functions to succeed in their role.
Top CRM platforms for sales onboarding:
Sales enablement platforms
Dedicated platforms centralize training materials, sales content, and performance tracking. They provide structure and measurability that scattered resources cannot match.
Here’s a quick comparison of top sales enablement platforms:
Learning management systems (LMS)
An LMS provides structure for training content while tracking completion and comprehension. This becomes particularly valuable for compliance training and standardized curriculum delivery.
Here are some of the best LMS tools for sales teams:
Sales onboarding templates and checklists (Free downloadable PDFs)
Ready-to-use sales onboarding templates and checklists accelerate program development and ensure comprehensive coverage of essential topics. These frameworks provide starting points that you can customize for your specific needs.
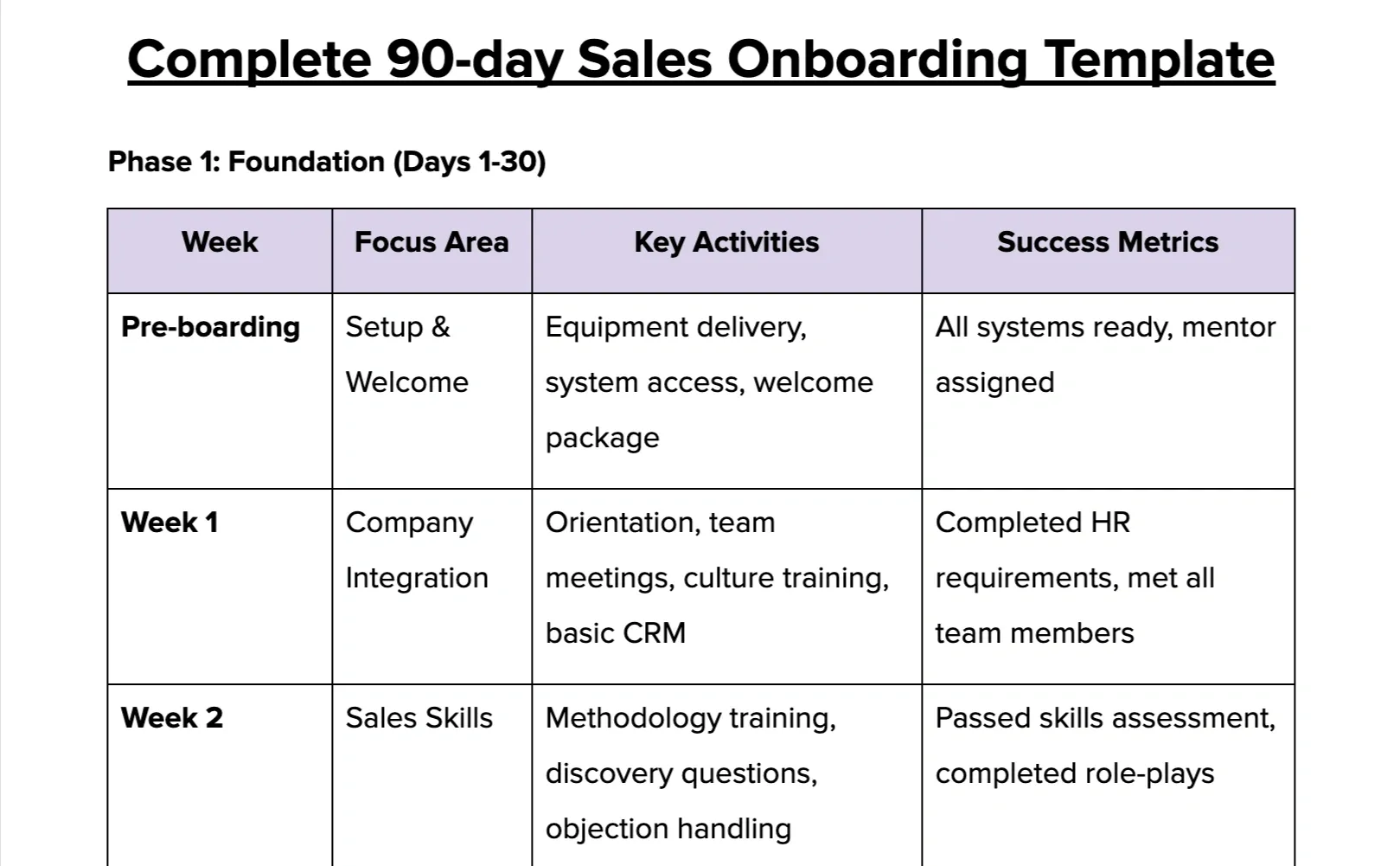
1. Complete 90-day sales onboarding template
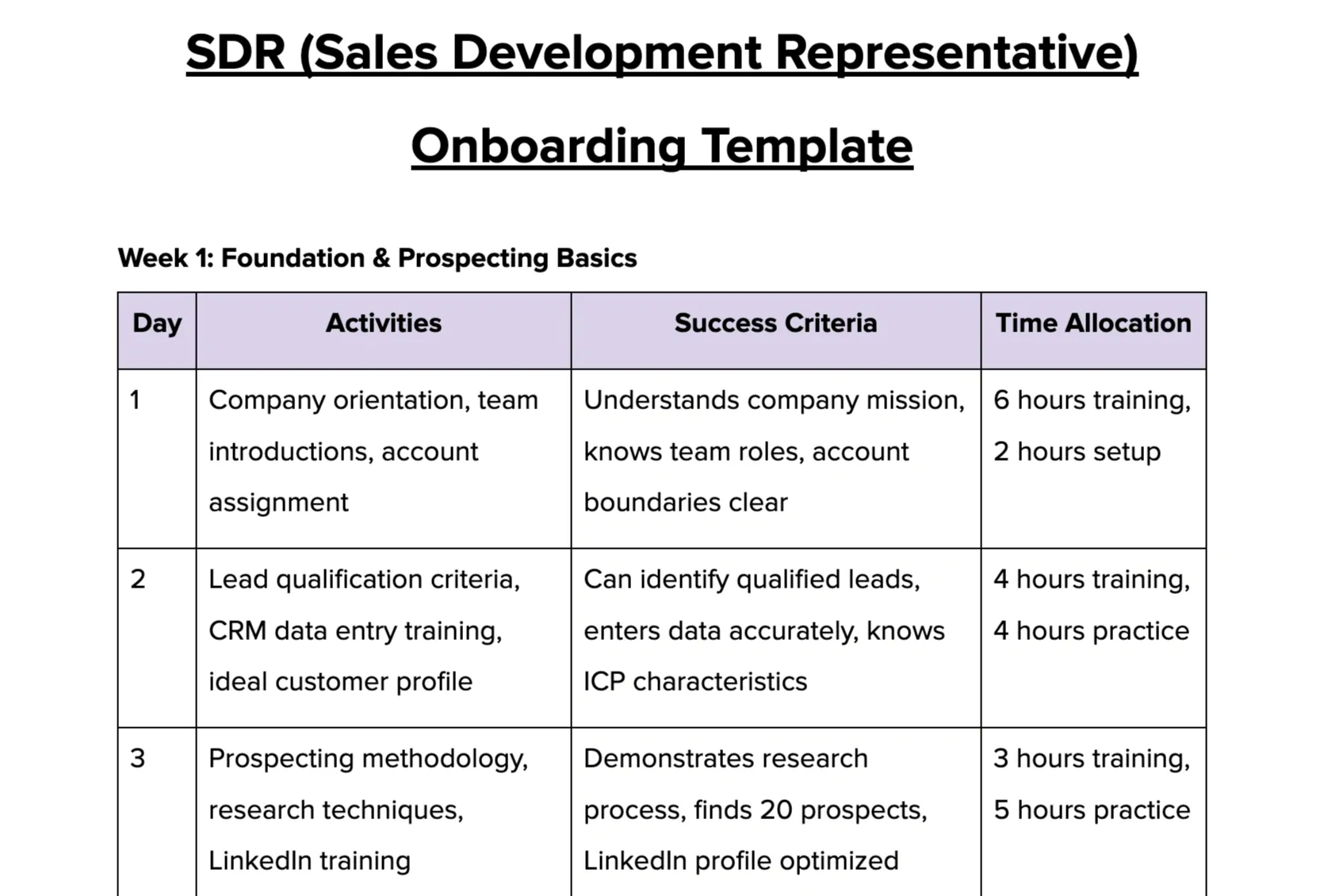
2. SDR onboarding template
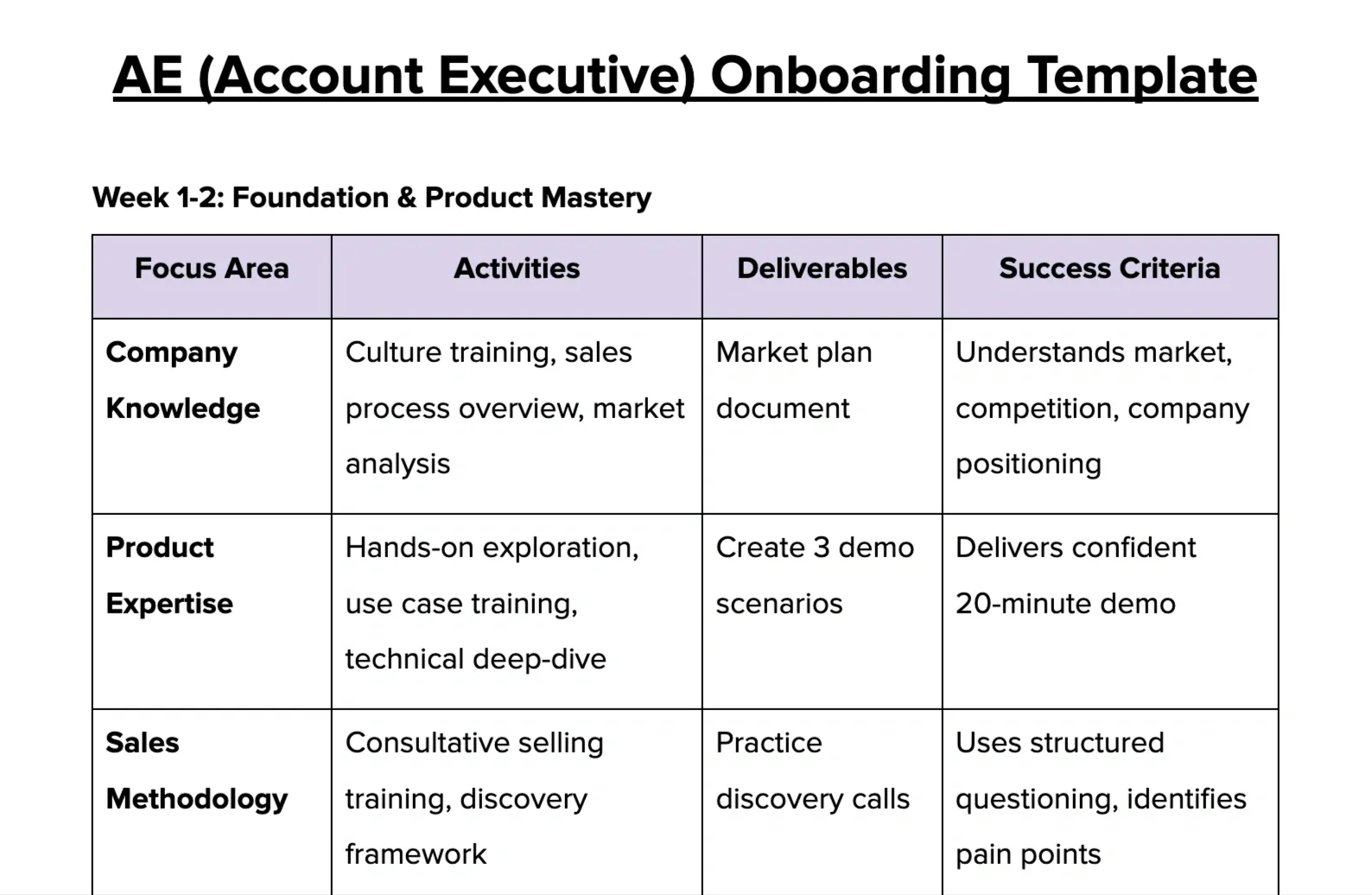
3. AE (Account Executive) Onboarding Template
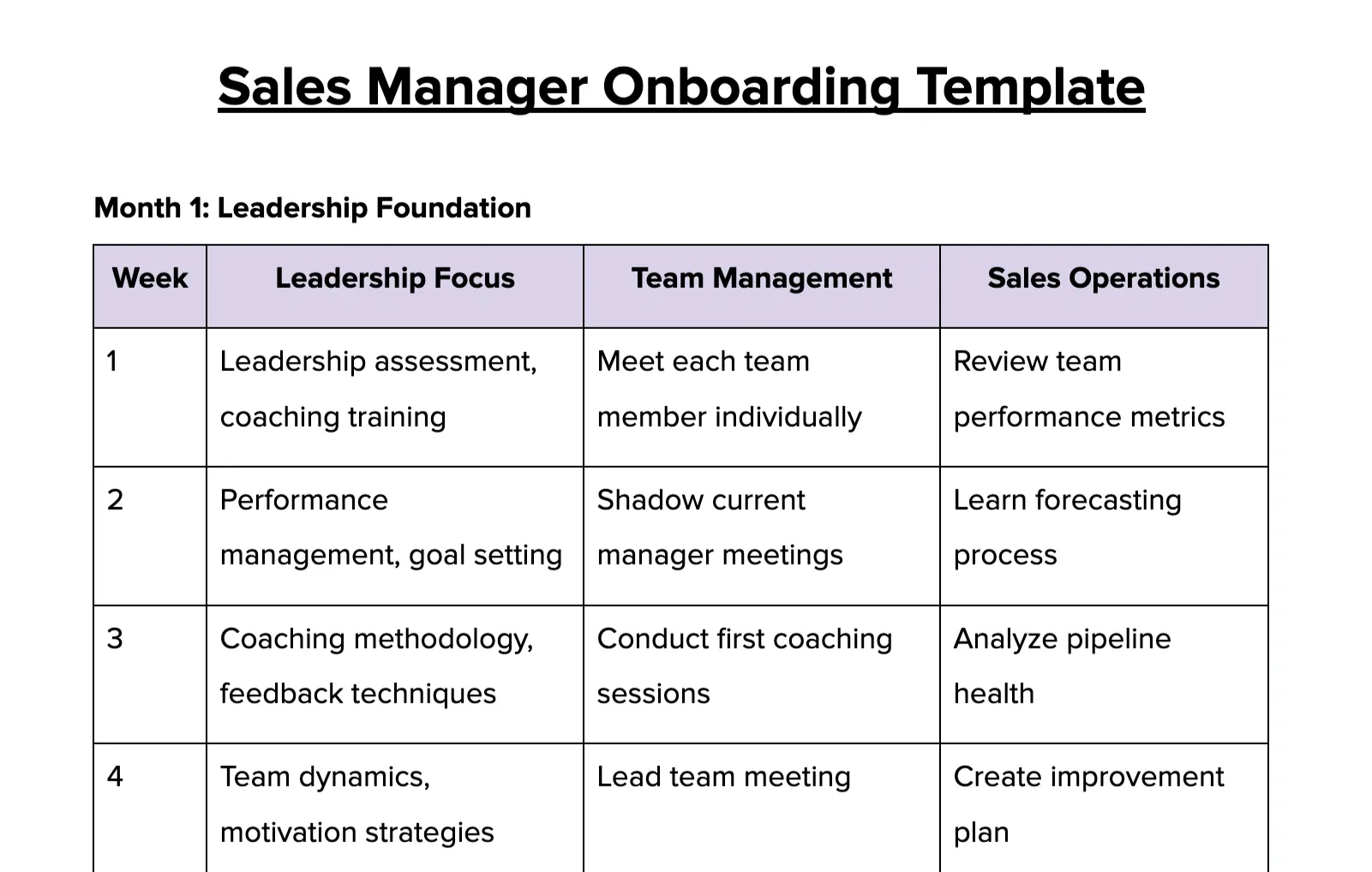
4. Sales Manager Onboarding Template
5. Pre-Boarding Preparation Checklist

6. Technology Setup Checklist

Conclusion
An effective sales onboarding process takes planning and ongoing refinement, but the return is clear: faster ramp times, stronger performance, and higher retention that directly impact revenue.
The best programs don’t just deliver information—they give reps opportunities to practice. Combining structured learning with interactive application ensures new hires gain confidence, not just knowledge.
As teams grow and become more distributed, tools like Supademo make it easy to scale this approach with guided demos and self-serve training that reps can access anytime.
Organizations like Greenpeace CEE have already seen the impact: by using Supademo to onboard employees onto internal tools, they strengthened digital literacy, reduced IT support time by over 40 hours in just three months, and improved readiness across regions.
The same approach can help you ramp up new sales reps faster, close knowledge gaps, and create a more confident, productive team from day one.
Ready to accelerate your onboarding? Start building interactive training with Supademo today!
Frequently asked questions
What is the sales onboarding process?
Sales onboarding is your structured program for integrating new sales hires into your organization. It covers company knowledge, product expertise, sales skills, and technology mastery over 60-90 days.
Why is sales onboarding important?
Effective onboarding reduces time-to-productivity and improves first-year retention. Well-onboarded reps also perform better than those who learn informally.
What are the key steps or phases in a sales onboarding process?
There are different phases in the sales onboarding process, including pre-boarding preparation, company orientation, sales training, product mastery, technology training, mentorship and shadowing, ongoing support, and regular evaluation. Each phase builds on the previous one.
What are the best practices for sales onboarding?
Create structured plans with self-serve elements, use varied training methods including interactive demos, integrate technology early, set clear expectations, provide continuous feedback, and foster supportive team environments.
How long should sales onboarding take?
Simple products need 30-45 days, moderate complexity requires 60-75 days, and enterprise solutions need 90-120 days. The key is balancing thoroughness with early productivity.
How can I create an effective sales onboarding program?
Start by defining clear objectives and success metrics. Map out a phase-based curriculum, gather necessary resources and tools, assign mentors, create measurement systems, and continuously improve based on feedback and results.